The Internet of Things (iot 4.0) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) both use the networking of smart devices & cloud computing to produce an always-online network that exchanges data to make educated decisions.
As a result, you no more need to monitor your home appliances, and businesses no longer require the services of thousands of employees to complete tasks that machines can complete.
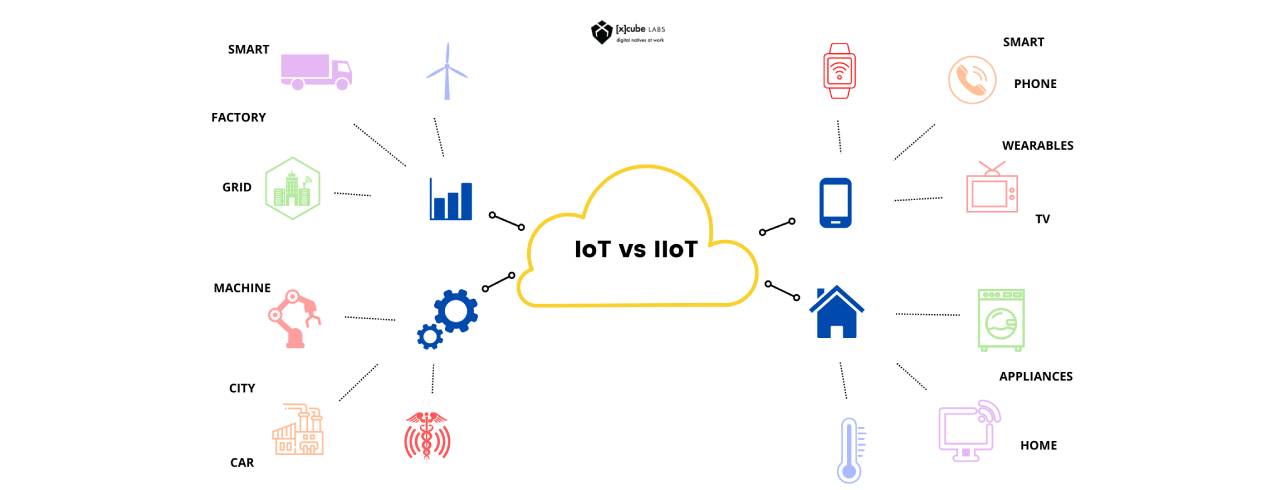
It is a network of intelligent devices that possess its computing capability. These devices are connected to form systems that, on an industrial scale, collect, monitor, exchange, & analyze data.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) is primarily focused on commercial and industrial applications, including but not limited to industry, power plants, agriculture, and oil and gas.
The Internet of Things includes the Industrial Internet of Things as a component or a subset of its overall scope; in other words, IIOT falls under iot significant, which is primarily concerned with applications in the business world. Intelligent devices play an essential part in IIOT, which helps in features providing vital information and analyzing and capturing data in real-time.
This is made possible by IIOT. With the help of IIOT, business choices can be taken more quickly and accurately. Additionally, IIOT assists in the expansion of companies by helping them better comprehend their business processes, which leads to those processes becoming more effective.
It is all about network communication that has its own distinct identities and networks linked to the Web. These devices will be fitted with China's IoT products, electronics, and software that will enable them to collect and exchange data with no intervention from a human being.
The primary objective of the Internet of Things (IoT industry 4.0) is to transform a "dumb" device, which is incapable of processing data, into a "smarter" device, which is capable of processing data on its own and has its computing capacity.
This will enable dumb devices to communicate real-time data and share data over the internet. By utilizing iot 4.0, you will be able to connect to the internet various things that are a part of your regular life, such as your thermostat, irrigation systems, kitchen appliances, and television.
An example of an Internet of Things gadget is a Bluetooth 5.0+ low energy module. It is a powerful SoC-based Bluetooth low energy module combining advanced features and minimizing current. It is an all-in-one module, including a superset of the most prominent nRF52® Series features, like Bluetooth LE Audio, Bluetooth Direction Finding, Bluetooth Long Range, and more, which makes it the ideal choice for LE Audio, professional lighting, advanced wearables, and other complex IoT applications.
You may devote your time and energy to your job, family, or continued education instead. They can reorganize their staff into various skill sections to bring value to their businesses when it comes to industries.
When comparing IoT with IIoT, there are a few concrete parallels that are important to be aware of, and they are as follows:
● The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the Internet of Things (IoT) both require a resource that is an internet connection that is both high-speed and inexpensive.
● You will need Internet of Things (IoT) tools and platforms to create software or applications, regardless of whether you plan to implement iot in logistics, industries, or homes.
● Both the IIoT and the industry 4.0 iot use a few I/O devices common to both, such as high-definition cameras. These microphones employ beamforming technology, GPS, geo-fencing technology, temperature monitoring, & water droplet sensors.
● To make intelligent decisions, AI and ML are prerequisites for both IoT and IIoT.
The Industrial Internet of Things and the Internet of Things have a few key distinctions. These include:
The Internet of Things in the Industrial World focuses on businesses like oil and gas production and power plants, including manufacturing facilities. On the other hand, the Internet of Things is primarily concerned with the homes and offices of individual consumers.
The Industrial Internet of Things is designed for large-scale applications, as well as its results have the potential to serve millions of customers. On the other hand, the IoT is designed for home automation on a more modest scale that helps make the lives of a family or a small group of individuals more comfortable.
The Industrial Internet of Things uses thousands of different instruments, such as sensing elements, MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) sensors, speed sensor systems, RFID sensors, torque sensors, and so on.
In order for IIoT to function correctly, large-scale networking systems are required. This will allow production managers to monitor their facilities from company headquarters remotely. Additionally, real-time & remote programming capabilities are included with IIoT applications. Troubleshooting issues with an industrial IoT system requires an in-house IIoT programmer.
Robust cyber security measures are required for the infrastructure of IIoT, such as SSL encryption, data encryption while in transit and while stored, data encryption while at rest, visual monitoring of servers, closed-loop systems, & biometric login.
IoT Production Line vs. IIoT Production Line
The instruments, sensors, and gadgets used in IIoT applications need to tolerate high temperatures, high speeds, and filthy conditions. As a result, the producers ensure that the devices can withstand severe use. Additionally, the infrastructure of the cloud and the network requires frequent maintenance.
· How are IoT and IIoT related?
IoT gadgets include home technology, fitness trackers, and other applications that generally don't generate emergency problems if something goes wrong. IIoT apps, on the other hand, connect equipment and devices in such areas as oil and natural gas, utilities & manufacturing.
· What is the difference between IoT production line and IIoT production line?
IoT Production Line vs. IIoT Production Line
The instruments, sensors, and gadgets used in IIoT applications need to tolerate high temperatures, high speeds, and filthy conditions. As a result, the producers ensure that the devices can withstand severe use. Additionally, the infrastructure of the cloud and the network requires frequent maintenance.
· What are the specific safety procedures of IIoT?
Robust cyber security measures are required for the infrastructure of IIoT, such as SSL encryption, data encryption while in transit and while stored, data encryption while at rest, visual monitoring of servers, closed-loop systems, & biometric login.
The comparison of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the Internet of Things (IoT technologies) that was just done offer you a good understanding of how the Internet of Things technology can be implemented in consumer and commercial settings differently. If you are new to the Internet of Things industry, you can contact ble module to make use of these various learning resources related to the IoT.